What Is Bitcoin? The First Cryptocurrency Explained
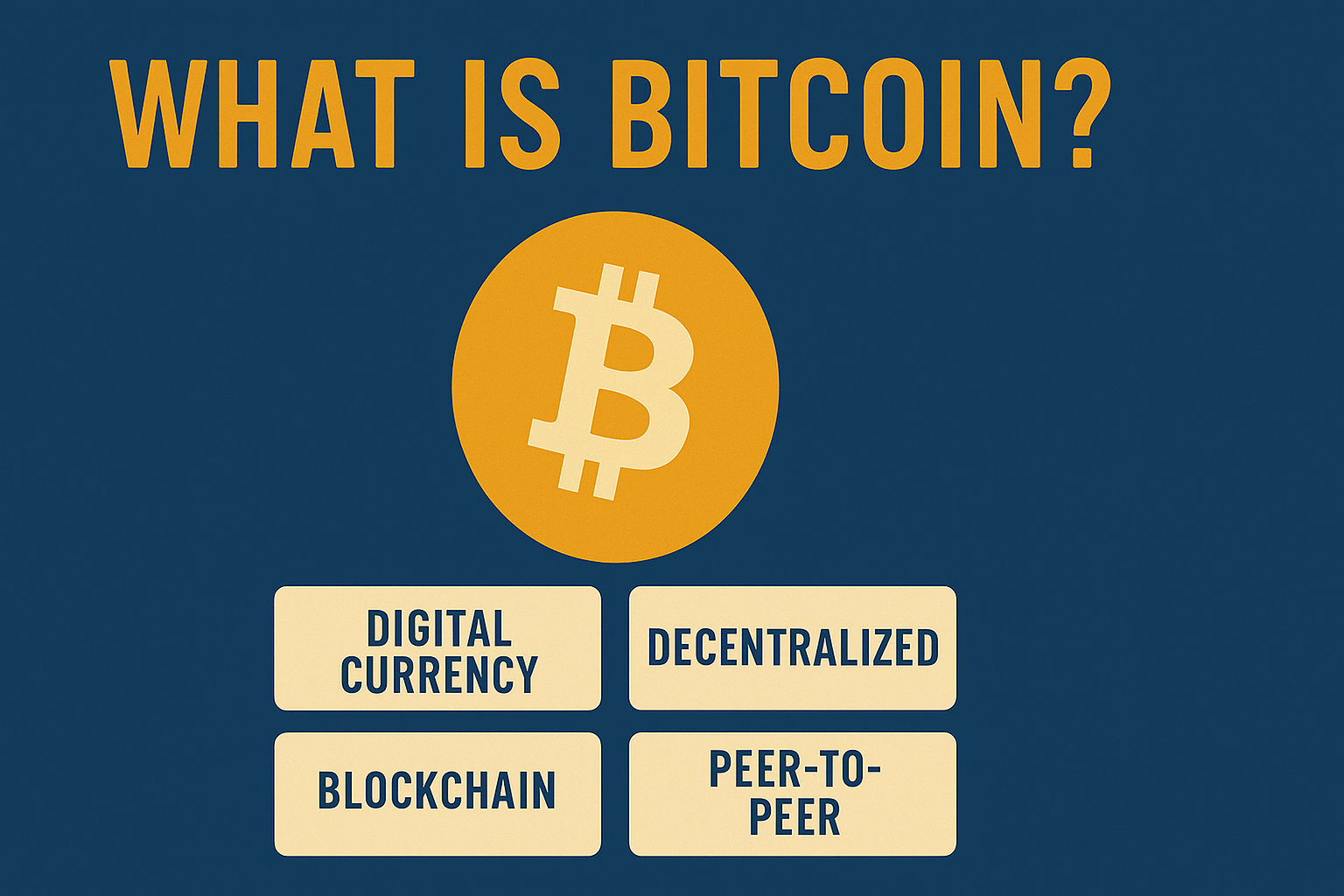
Bitcoin is often hailed as the pioneer of digital currency—a groundbreaking invention that has reshaped how we think about money. Created in 2009 by an anonymous figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin introduced the world to the concept of cryptocurrency: money that exists purely in digital form, without a central authority like a bank or government.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of computers using a technology called the blockchain. This is a public ledger that records every Bitcoin transaction ever made. Instead of relying on banks to verify transactions, Bitcoin uses a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work, where powerful computers solve complex puzzles to add new blocks of transactions.
Once a block is confirmed, it’s permanently added to the blockchain, ensuring transparency and security.
Key Features of Bitcoin
🔐 Decentralization
No single entity controls Bitcoin. It is maintained by a global community of miners and developers.
📉 Limited Supply
Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist, making it a deflationary asset—similar to gold in scarcity.
💱 Peer-to-Peer Transactions
Users can send Bitcoin directly to each other without intermediaries, often with lower fees and faster speeds.
🌍 Global Accessibility
Anyone with an internet connection can use Bitcoin, offering financial services to people in underbanked regions.
Why Is Bitcoin Valuable?
Bitcoin derives its value from several factors:
- Scarcity (limited supply)
- Utility (easy to transfer and store value)
- Security (impossible to counterfeit)
- Market Trust (growing adoption and investment)
While volatile, Bitcoin has been referred to as “digital gold” because many investors view it as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
Challenges and Criticism
Despite its promise, Bitcoin has faced several criticisms:
- Energy Consumption: Mining uses significant electricity.
- Volatility: Prices can swing wildly within hours.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Different governments treat Bitcoin differently, from acceptance to outright bans.
The Future of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has already made history and continues to evolve. Whether it becomes a standard form of payment or remains a digital store of value, its impact on technology and finance is undeniable.